Our Latest Corporate Social Responsibility Updates
April 24, 2025
First Quarter 2025 Update

Presenting our 2024 CSRD Report (ESG Report)
In Chapter 3 of the French Universal Registration Document (Declaration of Extra-financial Performance), we share our progress on our integrated sustainability strategy, prepared in alignment with the EU Corporate Sustainability Directive (CSRD) regime.
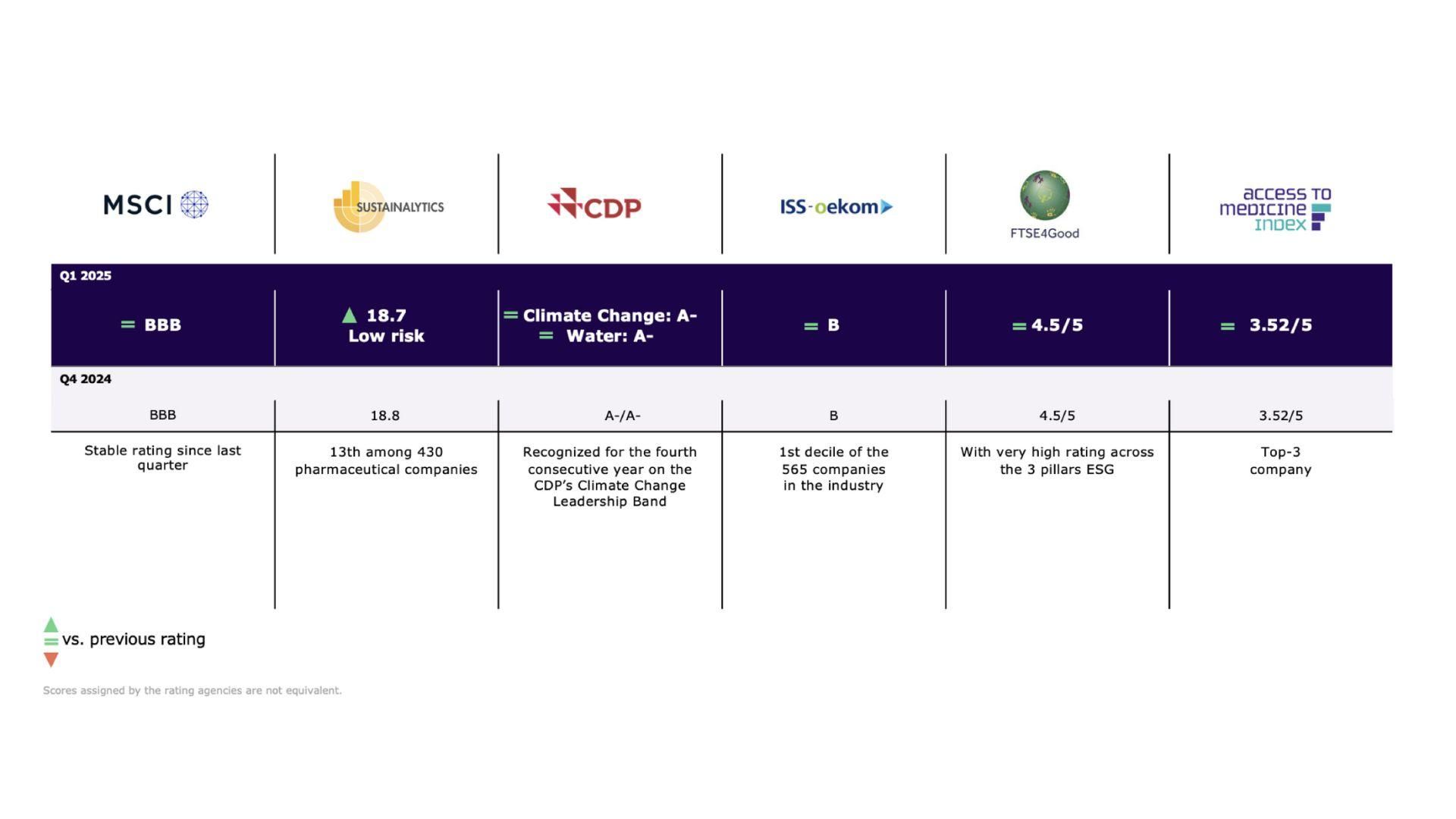
Environmental, Social and Governance Performance
ESG and commercial considerations are intrinsically linked and ongoing progress in our ESG performance is vital for Sanofi to succeed and grow in a sustainable way.

Leading the Way for Sustainable Finance
Sanofi is a pioneer of sustainable finance, with two Sustainability-linked Revolving Credit Facilities since 2020 and a Sustainability-Linked Bond, linked to its Global Health Unit, since 2021.
Product litigations
Information on Sodium Valproate (Depakine)
Information on Dengvaxia®
For most recent ESG information, see also our:
Quarterly results
ESG information throughout the quarterly results presentations and in the quarterly press releases
ESG Key Performance Indicators (Excel)
See our key ESG Performance Indicators
Global Reporting initiative (GRI) Index
See our GRI Index table
Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) index
See our SASB Index table

Our US Prescription Medicine Pricing Principles
We work passionately to prevent, treat and cure illness and disease, understand and solve healthcare needs of people across the world, and transform the practice of medicine.

Quick links

Corporate Governance

Reports and Publications
Financial calendar